10 Powerful ArcGIS Features Every GIS Professional Should Know
November 5, 2024 2024-11-05 10:3210 Powerful ArcGIS Features Every GIS Professional Should Know
10 Powerful ArcGIS Features Every GIS Professional Should Know
As Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology continues to evolve, ArcGIS remains one of the leading platforms for spatial data analysis, mapping, and decision-making. For GIS professionals, mastering ArcGIS’s core features can unlock powerful insights, streamline workflows, and enhance project outcomes. Here are ten essential ArcGIS features every GIS professional should know.
Related: Top ArcGIS Training Resources to Boost Your Skills in 2024

1. ArcGIS Online
ArcGIS Online is the cloud-based GIS platform that enables users to create, share, and analyze spatial data collaboratively. With ArcGIS Online, professionals can create web maps, access curated data, and integrate third-party data layers from Esri’s extensive Living Atlas. It allows GIS professionals to share insights through interactive maps and applications that are accessible anywhere with internet connectivity, making it ideal for team projects and public sharing.
Related: ArcGIS Online: Collaborative Mapping and Storytelling for GIS Professionals

2. Spatial Analysis Tools
The Spatial Analysis Tools in ArcGIS provide capabilities to perform complex analyses on geographic data. Tools like “Proximity,” “Overlay,” “Suitability Modeling,” and “Surface Analysis” allow users to uncover spatial patterns, relationships, and potential outcomes. For instance, a GIS professional can use proximity analysis to identify underserved areas based on distance to public facilities, a critical feature for urban planning and service provision.
3. ArcGIS Pro 3D Capabilities
3D GIS is increasingly important in fields like urban planning, real estate, and environmental management. ArcGIS Pro’s 3D capabilities enable users to visualize data in three dimensions, allowing for a more immersive and realistic view of landscapes, cityscapes, and underground resources. GIS professionals can analyze elevation, building heights, and visualize changes over time, enhancing their spatial understanding and ability to communicate complex scenarios effectively.
4. StoryMaps
ArcGIS StoryMaps offers a unique way to present spatial data with narrative context, combining maps, text, images, and multimedia. For professionals looking to communicate findings to a non-technical audience, StoryMaps is an excellent tool. It provides a visually engaging way to tell stories with data, making it ideal for educational materials, reports, and presentations that need to engage and inform.
Related: How to Make Your First Interactive Map with ArcGIS StoryMaps

5. ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World
The Living Atlas is a treasure trove of ready-to-use, authoritative datasets. Professionals can access a wealth of spatial information, including demographic, environmental, and real-time data on weather, traffic, and natural events. This curated data collection is continuously updated, enabling professionals to save time sourcing high-quality data and focus on analysis and decision-making.
Related: Discover Data and Maps on ArcGIS Living Atlas

6. Geocoding and Address Matching
Geocoding converts addresses into spatial data, placing them as points on a map. ArcGIS’s Geocoding tools support single or batch address matching, making it easy to create maps with client locations, service areas, or event occurrences. This feature is especially useful for professionals in logistics, retail, and public health, where location data analysis is essential.
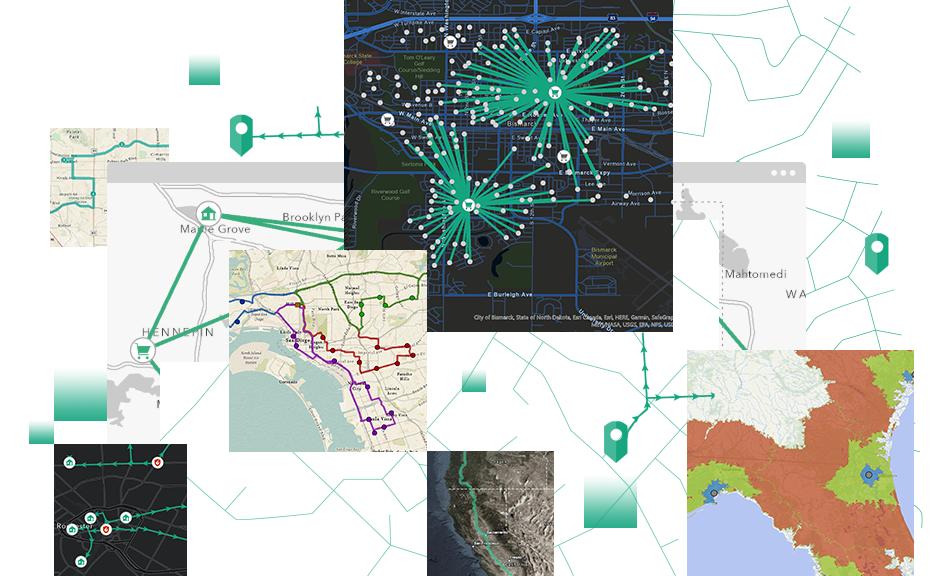
7. Network Analysis
The Network Analysis tools in ArcGIS enable professionals to solve complex transportation and routing problems. It includes capabilities such as finding the shortest path, determining the closest facility, and calculating service areas. This feature is invaluable for urban planners, emergency responders, and logistics managers who rely on efficient routing and accessibility information.
Related: 3 Things ArcGIS Network Analyst Can Do for You
8. ModelBuilder
For automating repetitive tasks, ModelBuilder is an essential ArcGIS tool. It allows GIS professionals to create visual workflows, or “models,” that automate multi-step processes. By dragging and dropping tools, users can set up complex workflows to handle tasks like data cleaning, analysis, and reporting. ModelBuilder is a powerful tool for increasing productivity, especially in projects with repetitive steps.
9. ArcGIS Dashboards
ArcGIS Dashboards provide a dynamic way to visualize and monitor key data in real-time. These dashboards can display maps, charts, gauges, and real-time data feeds, making them valuable for monitoring operations, public health data, or emergency responses. ArcGIS Dashboards allow users to customize displays, providing an intuitive way for decision-makers to access and interpret essential data quickly.
Related: Five Tips to Improve Your ArcGIS Dashboards
10. Python and ArcPy Integration
Python scripting, through ArcPy, enables professionals to automate tasks, perform custom analysis, and extend ArcGIS capabilities. With Python, GIS users can script workflows, customize tools, and streamline processes, making it a crucial skill for those looking to maximize ArcGIS’s potential. For example, a professional can use ArcPy to automate map production or complex spatial analyses, saving hours of manual work.
Mastering these ArcGIS features equips GIS professionals with the tools they need to tackle diverse spatial challenges effectively. Learn more here: https://ea-store.esri.com/en-ke/store/overview