10 Ways GIS is Transforming Agriculture in East Africa
September 18, 2024 2024-09-18 8:5310 Ways GIS is Transforming Agriculture in East Africa
10 Ways GIS is Transforming Agriculture in East Africa
Agriculture is the backbone of East Africa’s economy, employing a large proportion of the population and contributing significantly to GDP. As the region grapples with challenges such as climate change, population growth, and food security, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have emerged as a game-changer in the agricultural sector. By providing tools for data collection, analysis, and visualization, GIS enables farmers, policymakers, and stakeholders to make informed decisions. Here are ten ways GIS is transforming agriculture in East Africa, including a real-world example from Uganda.
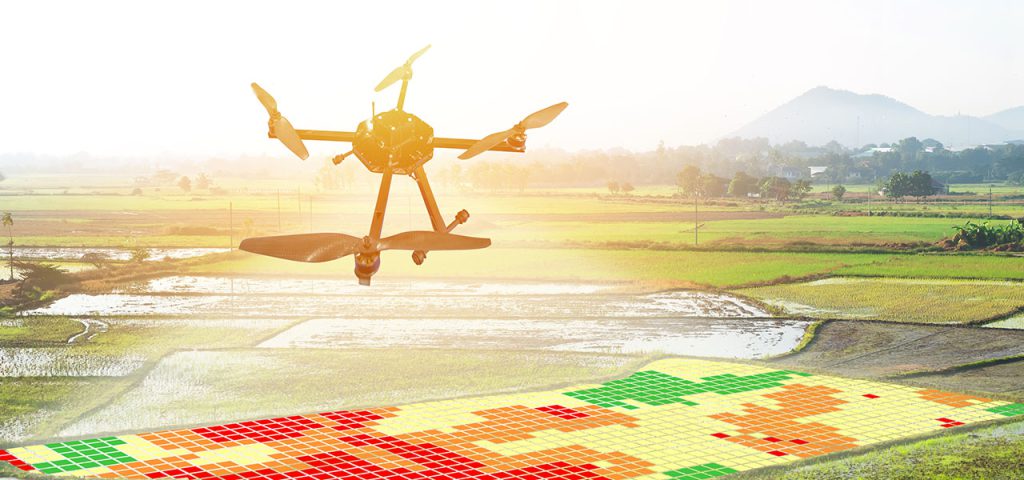

1. Precision Farming for Optimal Resource Use
GIS technology allows farmers to practice precision farming, which involves the use of data to manage fields at a micro-level. By using GIS tools to analyze soil properties, weather conditions, and crop requirements, farmers can optimize the use of resources like water, fertilizers, and pesticides. This leads to higher yields, reduced costs, and minimized environmental impact. In East Africa, where resources can be scarce, precision farming through GIS has proven vital for sustainable agriculture.
Related: Enhancing Precision Agriculture with GIS Technology
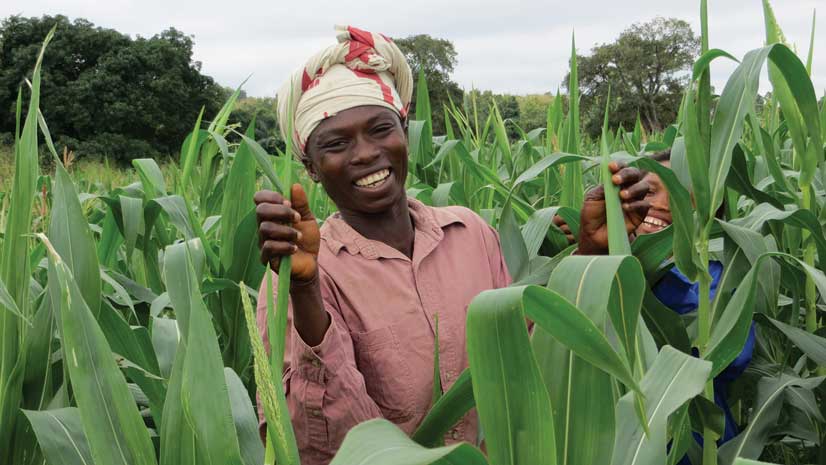

2. Monitoring Crop Health
GIS applications, in conjunction with remote sensing technology, enable the monitoring of crop health across large areas. By using satellite imagery and drones equipped with sensors, farmers can detect early signs of diseases, pest infestations, and water stress. This timely information allows for swift intervention, reducing crop loss and ensuring food security. In Uganda, for example, GIS technology is used to monitor coffee plantations to ensure that diseases such as coffee leaf rust are detected early.
3. Safeguarding Coffee Farmers in Uganda
An example of GIS in action is the initiative by Uganda Flying Labs to safeguard coffee farmers against risks. Using drones equipped with multispectral cameras and GIS software, they map coffee plantations to assess crop health. The data collected is used to identify areas affected by pests and diseases, helping farmers take preventative measures. This initiative not only protects the livelihood of farmers but also ensures the sustainability of Uganda’s coffee industry. You can read more about this innovative approach here.

4. Soil Mapping for Improved Crop Yields
Soil health is a critical factor in agricultural productivity. GIS enables detailed soil mapping, which involves the analysis of soil properties such as texture, composition, pH, and nutrient levels. In East Africa, soil maps guide farmers in selecting suitable crops, determining fertilizer requirements, and adopting appropriate land management practices. By understanding soil variations within a field, farmers can enhance crop yields and promote sustainable land use.
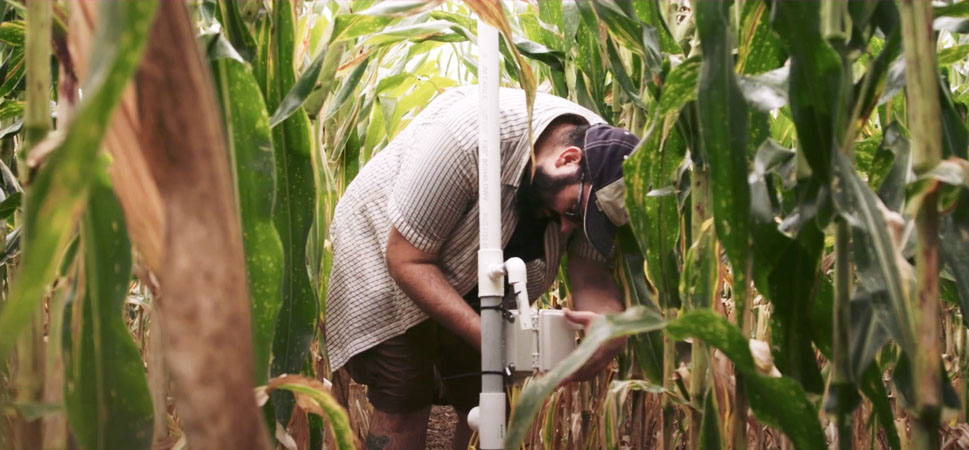

5. Enhancing Water Management
Water scarcity is a significant challenge in many parts of East Africa. GIS plays a crucial role in managing water resources by mapping water sources, analyzing irrigation systems, and monitoring water usage. Farmers can use GIS to plan efficient irrigation schedules, ensuring that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time. This not only conserves water but also improves crop productivity, especially in drought-prone areas.
6. Climate Change Adaptation
East Africa is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including erratic rainfall and rising temperatures. GIS helps farmers adapt to these changes by providing data on weather patterns, soil moisture levels, and climate trends. By analyzing this information, farmers can implement adaptive strategies such as selecting climate-resilient crop varieties, adjusting planting dates, and employing water conservation techniques.
7. Supporting Agricultural Planning and Policy
GIS provides valuable insights for agricultural planning and policymaking. By mapping agricultural activities, land use, and environmental conditions, GIS helps governments and organizations develop effective agricultural policies and land management plans. For instance, GIS data can identify areas suitable for agricultural expansion, assess the impact of farming practices on natural resources, and monitor the effectiveness of agricultural interventions.
8. Market Access and Supply Chain Management
Farmers in East Africa often face challenges in accessing markets and managing supply chains. GIS aids in mapping transportation networks, analyzing market locations, and identifying potential distribution routes. By providing this information, GIS helps farmers optimize the supply chain, reduce transportation costs, and connect with markets more efficiently. This is particularly important for perishable crops, where timely delivery is crucial to minimize losses.
9. Disaster Risk Management
Natural disasters such as floods, droughts, and landslides pose significant risks to agriculture in East Africa. GIS is instrumental in disaster risk management by mapping hazard-prone areas, assessing vulnerability, and monitoring environmental changes. Early warning systems based on GIS data can alert farmers to impending disasters, allowing them to take preventive measures such as relocating livestock, securing assets, or harvesting crops early.
10. Empowering Small-scale Farmers with Knowledge
In East Africa, small-scale farmers constitute most of the agricultural workforce. GIS technology empowers these farmers by providing them with access to critical information. Through mobile applications and community training programs, farmers can access GIS-based weather forecasts, crop management advice, and market information. This knowledge enables them to make informed decisions, improve productivity, and enhance their livelihoods.
Related: Helping farmers see the bigger picture.
Ready to transform your agricultural practices with the power of GIS? Discover how ArcGIS products can help you optimize your farming operations, enhance productivity, and safeguard your crops against risks. Visit our online store today to explore a wide range of ArcGIS solutions tailored for East African agriculture.