5 Ways ArcGIS Can Improve Conservation Efforts in Biodiversity Hotspots
November 4, 2024 2024-11-04 14:005 Ways ArcGIS Can Improve Conservation Efforts in Biodiversity Hotspots
5 Ways ArcGIS Can Improve Conservation Efforts in Biodiversity Hotspots
Biodiversity hotspots, characterized by exceptional levels of species diversity, face immense threats from human activity, climate change, and habitat loss. Protecting these ecologically rich areas is essential for preserving global biodiversity, and ArcGIS, with its powerful spatial analysis and mapping capabilities, has emerged as a vital tool in supporting conservation efforts. Here are five ways ArcGIS can enhance conservation in biodiversity hotspots, allowing conservationists to make more informed, data-driven decisions.
Related: ArcGIS Tips for Tracking East Africa’s Migratory Wildlife

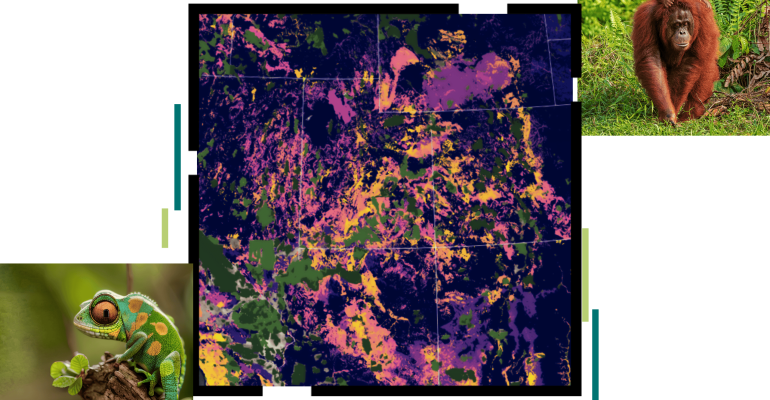
1. Mapping and Monitoring Habitat Loss
One of the most pressing issues in biodiversity hotspots is habitat loss due to deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture. ArcGIS allows conservationists to map land cover changes over time using satellite imagery and data from ArcGIS Living Atlas. By comparing historical and current maps, users can identify areas where habitats are shrinking and understand the rate of habitat loss. This information is crucial for prioritizing areas in need of immediate conservation interventions and for measuring the effectiveness of current preservation efforts.
Related: Digitally Transforming the Future of Natural Resources
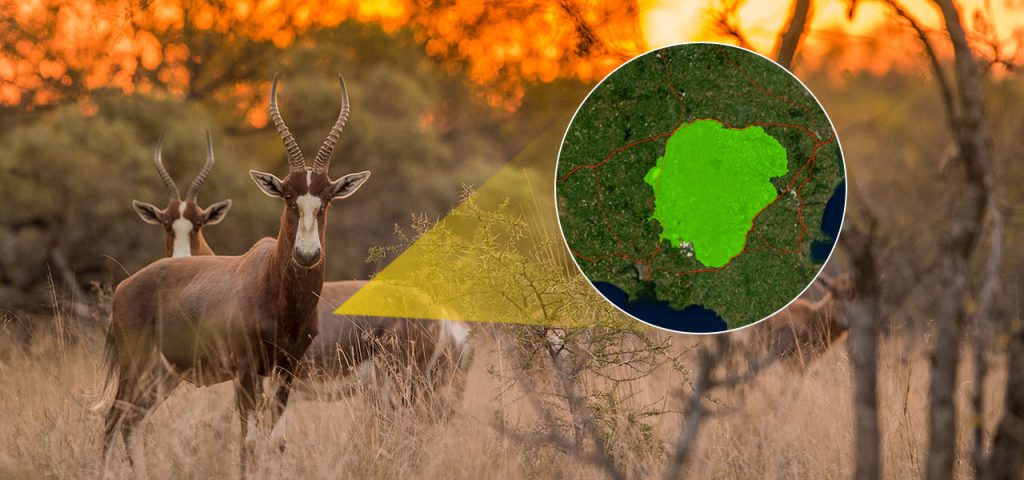
2. Species Distribution Modeling
Understanding where different species live within a hotspot is key to effective conservation. ArcGIS supports species distribution modeling by integrating data on species sightings, climate conditions, vegetation, and terrain. Tools like Suitability Modeling and Weighted Overlay in ArcGIS Pro allow users to identify areas with optimal conditions for specific species, helping conservationists locate critical habitats and design protected areas that support species’ needs. Such modeling helps prevent conflicts by ensuring habitats are safeguarded in the most biologically valuable areas.
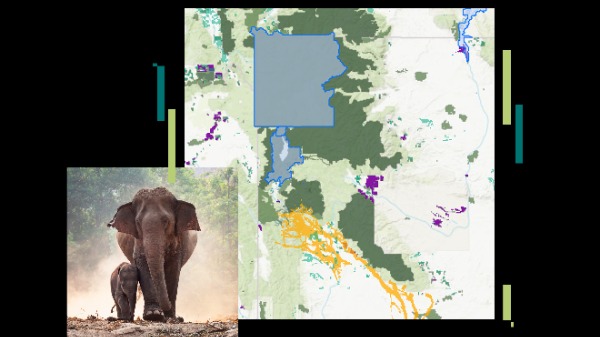
3. Hot Spot Analysis for Threat Detection
ArcGIS’s Hot Spot Analysis tool identifies statistically significant clusters of high and low values within data, making it ideal for detecting patterns of illegal activities like poaching or logging. By analyzing spatial data on past incidents, conservation teams can pinpoint high-risk areas and allocate resources effectively. This proactive approach allows for the strategic deployment of patrols, surveillance, and anti-poaching efforts, thereby enhancing the overall security of conservation zones.
4. Wildlife Corridor Planning
Connectivity between protected areas is crucial for species that need to move across large landscapes for breeding, foraging, or migration. ArcGIS’s Network Analysis and Least-Cost Path tools help conservationists map and plan wildlife corridors that link fragmented habitats. By identifying the most viable pathways between habitats, ArcGIS helps reduce the risk of inbreeding, maintains genetic diversity, and mitigates human-wildlife conflicts by guiding animals away from urban areas.
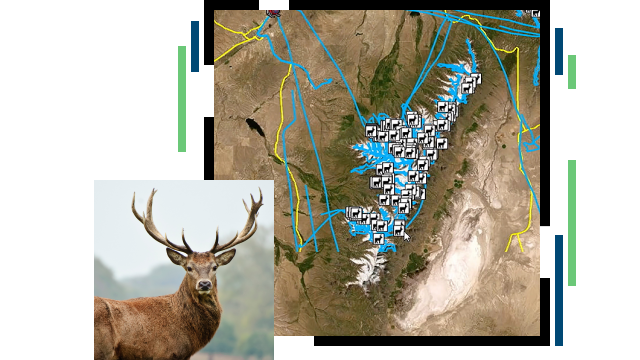
5. Climate Change Impact Analysis
Climate change poses significant threats to biodiversity by altering habitats and shifting suitable climate zones. Using climate data layers in ArcGIS, conservationists can analyze temperature and precipitation trends, identify vulnerable species and areas, and model future climate impacts. This enables proactive planning, helping conservationists implement strategies that address these challenges and ensure habitat resilience.
Related: ArcGIS for Climate Change Modelling: Innovative Approaches in 2024
ArcGIS provides essential tools that strengthen conservation efforts in biodiversity hotspots. By enabling habitat monitoring, species distribution mapping, threat detection, corridor planning, and climate change analysis, ArcGIS supports informed, data-driven strategies that maximize conservation impact. With these capabilities, ArcGIS is playing a vital role in safeguarding the world’s most vulnerable ecosystems and species.
Learn more here https://ea-store.esri.com/en-ke/store/overview