ArcGIS for Transportation: Cutting-Edge Solutions for 2024
August 29, 2024 2024-08-29 9:04ArcGIS for Transportation: Cutting-Edge Solutions for 2024
ArcGIS for Transportation: Cutting-Edge Solutions for 2024
As global transportation networks become increasingly complex, the need for advanced geospatial tools to manage, analyze, and optimize these systems has never been greater. ArcGIS continues to lead the way in providing innovative solutions for transportation planning, management, and operations. In 2024, ArcGIS offers a suite of cutting-edge tools designed to address the challenges faced by transportation professionals, from enhancing safety and efficiency to supporting sustainable development.
This blog post explores how ArcGIS is transforming the transportation sector in 2024, with a focus on the latest solutions that are helping to shape the future of mobility.
The Role of GIS in Transportation
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have long played a crucial role in transportation, enabling professionals to visualize and analyze spatial data to improve decision-making. From mapping road networks and planning public transit routes to managing infrastructure assets and analyzing traffic patterns, GIS provides the spatial context needed to understand and optimize transportation systems.
In 2024, the integration of advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, and real-time data analytics with GIS is taking transportation planning and management to new heights. ArcGIS, with its robust platform and tools, is at the forefront of this transformation, offering solutions that address the unique needs of the transportation industry.
Related: GIS for Transportation Planning and Traffic Management
1. Smart Transportation Planning with ArcGIS Urban
Urbanization continues to drive the demand for smarter transportation solutions, and ArcGIS Urban is helping planners meet this demand. ArcGIS Urban is a web-based 3D application that allows transportation planners to visualize and analyze the impact of transportation projects within the broader urban context.
Key Features:
- Scenario Planning: Transportation planners can create multiple scenarios to explore different transportation infrastructure options, such as new roads, transit lines, or bike lanes. This allows for a more informed comparison of how each option impacts traffic flow, land use, and urban development.
- Public Engagement: ArcGIS Urban supports public engagement by providing easy-to-understand 3D visualizations that can be shared with stakeholders and the community. This transparency helps build public support for transportation projects.
- Integration with Other Data: ArcGIS Urban integrates seamlessly with other ArcGIS tools and data sources, enabling planners to incorporate environmental data, demographic trends, and economic factors into their analyses.
Example Use Case: A city planning department could use ArcGIS Urban to model the impact of a proposed light rail line. By comparing scenarios with and without the rail line, planners can assess its potential effects on traffic congestion, accessibility, and local development, helping them make data-driven decisions.
Related: Implementing ArcGIS Urban for Smart City Planning
2. Real-Time Traffic Management with ArcGIS Velocity
Managing traffic in real-time is a critical challenge for modern cities, and ArcGIS Velocity offers a powerful solution. ArcGIS Velocity is a real-time and big data analytics service that processes high-volume, high-velocity data streams to support dynamic decision-making.
Key Features:
- Real-Time Data Ingestion: ArcGIS Velocity can ingest data from various sources such as GPS devices, IoT sensors, and traffic cameras. This data is processed in real-time to provide up-to-the-minute insights into traffic conditions.
- Advanced Analytics: With built-in analytics tools, transportation managers can identify patterns, predict traffic congestion, and optimize traffic signal timings. These analytics can be used to implement dynamic traffic management strategies that adapt to changing conditions.
- Incident Detection and Response: ArcGIS Velocity enables rapid detection of incidents such as accidents or road closures. Automated alerts can be sent to relevant authorities, allowing for quick response and minimizing disruption.
Example Use Case: A city’s traffic management center could use ArcGIS Velocity to monitor traffic conditions across the city in real-time. By analyzing data from connected vehicles and traffic sensors, the system can automatically adjust traffic signals to alleviate congestion or reroute traffic in response to an accident, ensuring smoother traffic flow.

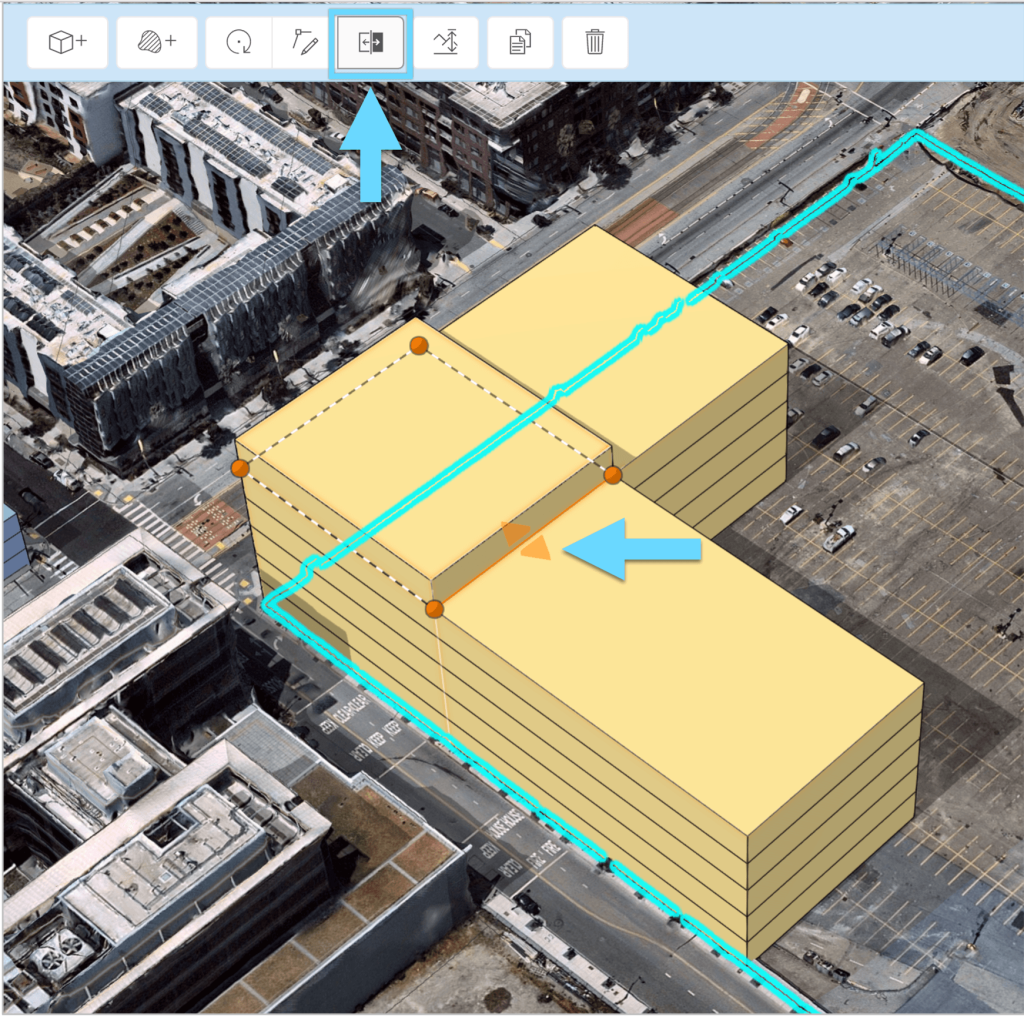
3. Infrastructure Asset Management with ArcGIS Field Maps
Maintaining transportation infrastructure is essential for safety and efficiency, and ArcGIS Field Maps is a critical tool for managing these assets. ArcGIS Field Maps is a mobile app that combines map viewing, data collection, and location tracking in a single application, making it ideal for field operations.
Key Features:
- Mobile Data Collection: Field crews can use ArcGIS Field Maps to collect data on infrastructure assets such as roads, bridges, and traffic signals directly from the field. The app supports offline data collection, ensuring that crews can work in remote areas without connectivity.
- Real-Time Data Syncing: Collected data is synced in real-time with the organization’s GIS, providing up-to-date information on the status and condition of infrastructure assets. This real-time syncing improves the accuracy and timeliness of maintenance activities.
- Inspection and Reporting: The app allows for detailed inspections, where field crews can record issues, take photos, and generate reports on the spot. These reports can be used to prioritize maintenance tasks and track the lifecycle of assets.
Example Use Case: A transportation agency responsible for highway maintenance could equip its field crews with ArcGIS Field Maps. Crews can conduct regular inspections of road conditions, document issues such as potholes or damaged guardrails, and immediately sync this data with the central GIS database. This enables the agency to prioritize repairs, schedule maintenance efficiently, and ensure road safety.
Related: How ArcGIS Field Maps Can Revolutionize Field Data Collection

4. Sustainable Transportation Planning with ArcGIS Green Infrastructure
As sustainability becomes a central concern in transportation planning, ArcGIS Green Infrastructure provides tools for integrating environmental considerations into transportation projects. This extension allows planners to incorporate green infrastructure—such as parks, wetlands, and greenways—into their transportation plans.
Key Features:
- Environmental Impact Analysis: Planners can analyze the environmental impact of transportation projects by assessing factors such as carbon emissions, air quality, and habitat disruption. This analysis helps in designing transportation systems that minimize environmental harm.
- Green Infrastructure Integration: ArcGIS Green Infrastructure facilitates the incorporation of green spaces into transportation networks. This includes planning for bike lanes, pedestrian paths, and public transit routes that are connected to green spaces, promoting sustainable mobility.
- Climate Resilience: The toolset also supports the design of transportation infrastructure that is resilient to climate change, such as flood-resistant roads and green corridors that mitigate urban heat islands.
Example Use Case: A regional transportation authority planning a new highway could use ArcGIS Green Infrastructure to assess its environmental impact. By identifying sensitive habitats and green spaces, the planners can modify the highway’s route to minimize disruption and integrate green infrastructure, such as wildlife crossings and green belts, to enhance sustainability.
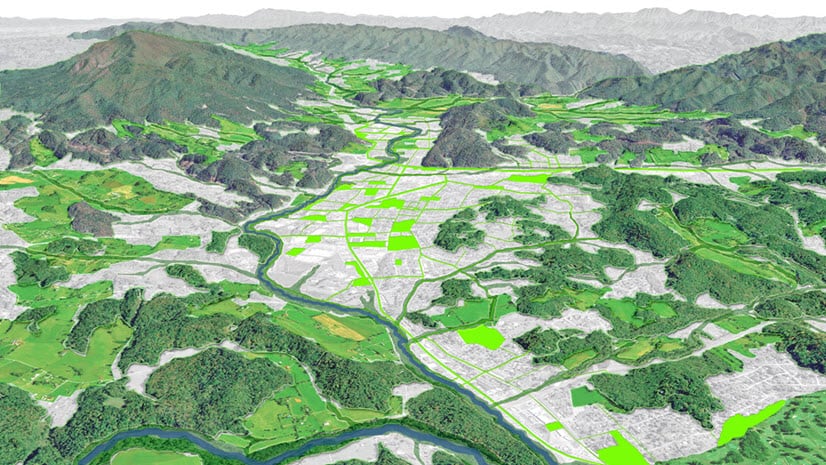
5. Public Transit Optimization with ArcGIS Network Analyst
Public transit systems are vital to urban mobility, and ArcGIS Network Analyst provides powerful tools for optimizing these systems. Network Analyst allows transportation planners to model and analyze transportation networks, helping to improve transit routes, schedules, and accessibility.
Key Features:
- Route Optimization: Network Analyst can optimize public transit routes based on factors such as travel time, distance, and ridership patterns. This ensures that transit services are efficient and meet the needs of the population.
- Service Area Analysis: Planners can analyze the service areas of transit stops, identifying gaps in coverage and ensuring that all communities have access to public transportation.
- Multimodal Analysis: The tool supports multimodal transportation analysis, allowing planners to design transit systems that seamlessly integrate with other modes of transportation, such as biking or walking.
Example Use Case: A city’s public transit agency could use ArcGIS Network Analyst to redesign its bus routes. By analyzing ridership data and optimizing routes for travel time and coverage, the agency can increase the efficiency of the transit system, reduce operating costs, and improve the overall rider experience.
From smart urban planning and real-time traffic management to infrastructure asset maintenance and sustainable transportation design, ArcGIS provides the tools needed to create and manage transportation networks that meet the needs of today while preparing for the challenges of tomorrow. By leveraging these solutions, transportation professionals can make informed decisions that enhance safety, efficiency, and sustainability, ultimately contributing to a more connected and resilient world.