ArcGIS Tips for Tracking East Africa’s Migratory Wildlife
September 19, 2024 2024-09-19 9:03ArcGIS Tips for Tracking East Africa’s Migratory Wildlife
ArcGIS Tips for Tracking East Africa’s Migratory Wildlife
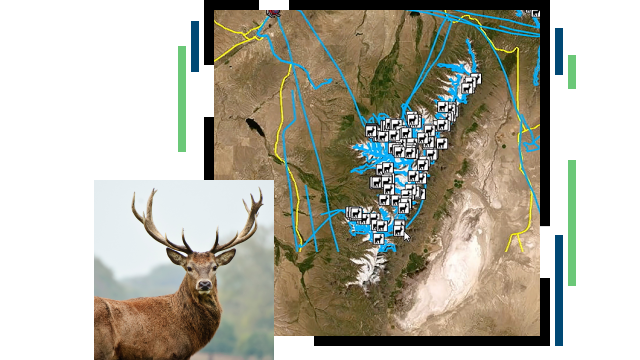
East Africa is renowned for its diverse and abundant wildlife, hosting some of the world’s most iconic migratory species, such as wildebeest, zebras, elephants, and various bird species. These migrations are not only a natural wonder but also play a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance of the region’s ecosystems. However, wildlife populations in East Africa face mounting pressures from habitat loss, poaching, climate change, and human-wildlife conflicts. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have become an invaluable tool in addressing these challenges, providing researchers and conservationists with the ability to monitor, analyze, and protect migratory wildlife. Here are some ArcGIS tips for effectively tracking East Africa’s migratory wildlife.

1. Utilize Real-Time Tracking for Immediate Insights
Real-time tracking is essential for monitoring the movements of migratory species and responding quickly to emerging threats. ArcGIS offers real-time data integration, allowing conservationists to gather location data from GPS collars, satellite tags, and other tracking devices attached to animals. This data can be visualized on interactive maps, providing immediate insights into the movement patterns and habitat use of migratory wildlife. For example, Kenya’s endangered rhinos are monitored using real-time tracking systems to safeguard them against poaching and other threats. By leveraging ArcGIS, conservationists can react promptly to protect these animals, as detailed in the real-time ecological monitoring article.
Read more: Real-Time Ecological Monitoring Safeguards Kenya’s Endangered Rhinos
2. Employ Spatial Analysis for Migration Corridor Identification
Migratory wildlife often relies on specific corridors to travel between habitats. Identifying and protecting these migration corridors is crucial for species survival. ArcGIS provides advanced spatial analysis tools that can analyze tracking data to pinpoint critical migration routes. By overlaying movement data with other spatial layers such as land use, vegetation cover, and human infrastructure, researchers can identify potential barriers and areas of conflict. This information is vital for developing strategies to maintain and restore these corridors, ensuring that migratory species can move freely across the landscape.

3. Integrate Remote Sensing for Habitat Monitoring
Remote sensing, when combined with ArcGIS, offers a powerful approach to monitor changes in wildlife habitats. Satellite imagery and aerial data can be used to assess vegetation cover, water availability, and habitat fragmentation over time. This is particularly important in East Africa, where habitat loss due to agricultural expansion, urban development, and climate change threatens migratory routes. By analyzing remote sensing data in ArcGIS, conservationists can identify habitat changes that may impact wildlife movements and implement measures to mitigate these effects.
4. Leverage ArcGIS Online for Collaborative Conservation Efforts
Wildlife conservation often requires a collaborative approach, involving multiple stakeholders such as governments, NGOs, and local communities. ArcGIS Online enables the sharing of maps, data, and analyses with a wide audience, facilitating collaboration and coordinated action. For instance, conservationists can create and share web maps highlighting the locations of migratory wildlife, protected areas, and potential conflict zones. These maps can be accessed by field teams, policymakers, and the public, fostering a collective effort to protect East Africa’s migratory species.

5. Use GIS for Human-Wildlife Conflict Mitigation
Human-wildlife conflict is a significant challenge in East Africa, especially in areas where migratory routes overlap with human settlements and agricultural lands. ArcGIS can help mitigate these conflicts by mapping hotspots where wildlife encroach on human activities. By analyzing patterns of movement and incidents of conflict, conservationists can develop strategies such as early warning systems, wildlife corridors, and community education programs. For example, mapping the seasonal movements of elephants can help farmers implement preventive measures to protect their crops during peak migration periods.
6. Employ ArcGIS StoryMaps to Raise Awareness
Raising public awareness is a key component of wildlife conservation. ArcGIS StoryMaps is an effective tool for creating engaging narratives that combine maps, images, and multimedia to tell the story of East Africa’s migratory wildlife. Conservation organizations can use StoryMaps to showcase the journeys of migratory species, highlight the challenges they face, and illustrate the conservation efforts underway to protect them. By making the data accessible and understandable to a broader audience, StoryMaps can inspire support for conservation initiatives and promote a deeper understanding of the importance of wildlife migration.
7. Implement Predictive Modeling for Proactive Conservation
ArcGIS allows for the integration of predictive modeling techniques to forecast future wildlife movements and habitat use. By combining historical tracking data with environmental variables such as rainfall, vegetation growth, and temperature, researchers can predict how migratory patterns may change in response to factors like climate change and habitat alteration. This proactive approach enables conservationists to identify potential future threats and implement measures to mitigate them, such as creating new protected areas or enhancing existing corridors.
8. A Holistic Approach to Wildlife Protection
A holistic approach to wildlife conservation involves addressing the interconnected aspects of ecosystems, communities, and wildlife. As highlighted in the holistic approach to protecting Africa’s wildlife, GIS plays a central role in this strategy by providing the tools to analyze ecological data, monitor threats, and engage stakeholders. ArcGIS can support holistic conservation efforts by integrating data on wildlife movements, habitat conditions, human activities, and conservation interventions into a unified platform, offering a comprehensive view of the conservation landscape.
Read more: A Holistic Approach to Protecting Africa’s Wildlife

9. Create Custom Dashboards for Wildlife Monitoring
ArcGIS Dashboards provide a dynamic platform for visualizing wildlife tracking data and monitoring key metrics. Conservationists can create custom dashboards that display real-time information on animal locations, movement patterns, and environmental conditions. These dashboards can include interactive charts, graphs, and maps, offering an intuitive way to monitor the status of migratory wildlife. Field teams can use these dashboards to make data-driven decisions and coordinate conservation actions effectively.
10. Enhance Community Engagement through Participatory Mapping
Engaging local communities is essential for the success of wildlife conservation in East Africa. Participatory mapping using ArcGIS empowers communities to contribute their knowledge of wildlife movements, habitat conditions, and conflict areas. By involving communities in data collection and map creation, conservationists can foster a sense of ownership and encourage local support for conservation efforts. This collaborative approach can lead to more sustainable and culturally sensitive solutions for protecting migratory wildlife.
Visit our online store to discover a range of ArcGIS products tailored for conservationists and researchers. Equip yourself with the tools you need to make a real impact in safeguarding the region’s iconic wildlife. Start exploring ArcGIS today and become a part of the solution for a sustainable future!