Enhancing Precision Agriculture with GIS Technology
June 21, 2024 2024-06-21 9:41Enhancing Precision Agriculture with GIS Technology
Enhancing Precision Agriculture with GIS Technology
The global agricultural sector is undergoing a transformative shift, driven by the need to increase productivity while ensuring sustainability. One of the most significant advancements facilitating this transformation is the integration of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology in precision agriculture. Precision agriculture leverages GIS to optimize field-level management concerning crop farming. This blog explores how GIS technology, particularly through ArcGIS, is revolutionizing precision agriculture and its impact on the agricultural industry.
Related: Uganda Flying Labs: Safeguarding Coffee Farmers Against Risk
Understanding precision agriculture
Precision agriculture is a farming management concept based on observing, measuring, and responding to inter and intra-field variability in crops. It aims to enhance agricultural productivity, reduce environmental impact, and ensure resource efficiency. The practice involves the use of various technologies, including GPS, sensors, drones, and, crucially, GIS.
The role of GIS in precision agriculture
GIS technology is integral to precision agriculture for several reasons:
- Spatial data management: GIS allows farmers to collect, manage, and analyze spatial and temporal data. This includes information on soil properties, crop health, weather patterns, and more.
- Mapping and visualization: Through GIS, farmers can create detailed maps that visualize various aspects of their fields. These maps can highlight areas requiring attention, such as zones with poor crop health or regions needing more irrigation.
- Analysis and decision-making: GIS provides tools for analyzing spatial data, helping farmers make informed decisions about planting, fertilizing, irrigating, and harvesting. This analysis can lead to more efficient use of resources and increased yields.
Related: Helping farmers see the bigger picture.

Key applications of GIS in precision agriculture
1. Soil mapping and analysis
Understanding soil properties is critical for effective crop management. GIS technology allows for detailed soil mapping and analysis, enabling farmers to identify variations in soil composition, moisture levels, and nutrient content. This information helps in making precise decisions about soil treatment and crop placement.
2. Crop monitoring
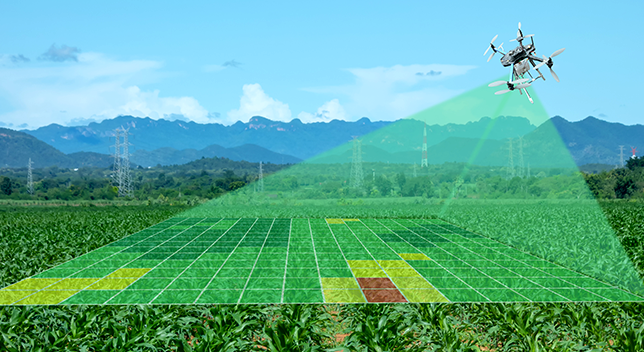
Using satellite imagery and drone data, GIS enables continuous crop monitoring. ArcGIS can process this data to detect changes in crop health, identify pest infestations, and monitor growth patterns. This real-time monitoring allows for timely interventions, improving crop health and yields.
3. Variable rate technology (VRT)
Variable Rate Technology involves applying inputs (such as fertilizers, pesticides, and water) at varying rates across a field, rather than a uniform application. GIS supports VRT by providing detailed maps that guide machinery in applying the correct amount of inputs in different areas, optimizing resource use and enhancing crop productivity.
4. Yield mapping and analysis
Yield monitors on harvesting equipment collect data on crop yield and quality. This data is integrated into GIS to create yield maps, showing the spatial variability of crop performance. These maps help farmers understand factors influencing yields and develop strategies for future planting seasons.
5. Irrigation management
Efficient water use is crucial in agriculture. GIS technology helps in designing and managing irrigation systems by analyzing soil moisture levels, weather forecasts, and crop water needs. This ensures that water is applied precisely where and when it is needed, conserving water and promoting healthy crop growth.
Related: Promoting Sustainable Agriculture

ArcGIS: Empowering Precision Agriculture
ArcGIS offers a comprehensive suite of tools tailored for precision agriculture. Here’s how ArcGIS enhances precision agriculture practices:
- ArcGIS Pro: This desktop GIS application provides advanced tools for spatial analysis and mapping. Farmers and agronomists can use ArcGIS Pro to create detailed field maps, analyze spatial data, and generate insights that guide agricultural practices.
- ArcGIS Online: ArcGIS Online allows users to store, share, and analyze geospatial data in the cloud. Farmers can access their data from anywhere, collaborate with stakeholders, and integrate various data sources for comprehensive analysis.
- ArcGIS Field Maps: This mobile app enables field data collection and real-time location tracking. It helps farmers gather on-the-ground data, update maps in real-time, and make informed decisions while in the field.
- ArcGIS Drone2Map: This tool processes drone-captured imagery into high-resolution maps and 3D models. It’s invaluable for crop monitoring, field mapping, and assessing crop health from above.
- ArcGIS Image Analyst: This extension provides advanced capabilities for image processing and analysis. It’s particularly useful for interpreting satellite and drone imagery, allowing for detailed crop monitoring and analysis.

GIS technology is a cornerstone of modern precision agriculture, offering tools and insights that drive efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. With platforms like ArcGIS, farmers can harness the power of spatial data to make informed decisions, optimize resource use, and improve crop yields. As the agricultural industry continues to evolve, the integration of GIS will undoubtedly play a crucial role in meeting the global demand for food in a sustainable manner.
Visit our online store to explore and purchase ArcGIS Products!