Maps and Apps Revolutionize Water Management in Arusha City
November 1, 2023 2023-11-01 13:09Maps and Apps Revolutionize Water Management in Arusha City
Maps and Apps Revolutionize Water Management in Arusha City
The Arusha Urban Water Supply and Sanitation Authority (AUWSA), entrusted with the responsibility of overseeing water supply and sewerage services in Arusha City, Tanzania, has embraced technological innovation to enhance operational efficiency. AUWSA’s mission centers around the efficient delivery of quality water and sanitation services using available resources and sustainable technologies.
In 2019, AUWSA embarked on a transformative journey by adopting ArcGIS, Esri’s comprehensive mapping and spatial analytics software. This transition was driven by the need for a robust Geographic Information System (GIS) package that could provide advanced capabilities for mobile data collection, visualization, and data management.

Enhancing nonrevenue water management through GIS
ArcGIS quickly became an indispensable tool for AUWSA, supporting various aspects of their operations, including asset management, customer service, network planning, and leakage repair. This powerful GIS system played a pivotal role in the utility’s quest to reduce nonrevenue water.
Before ArcGIS implementation, leakage data was not tracked in the GIS, and there was no comprehensive information about nonrevenue water. However, ArcGIS Collector was introduced to collect leakage data from the field, empowering plumbers and surveyors with the tools to report and document leakages. This involved comprehensive training, including office-based and field-based instruction. Even engineers embraced the Collector app, reporting leakages while working in the field or at the office.
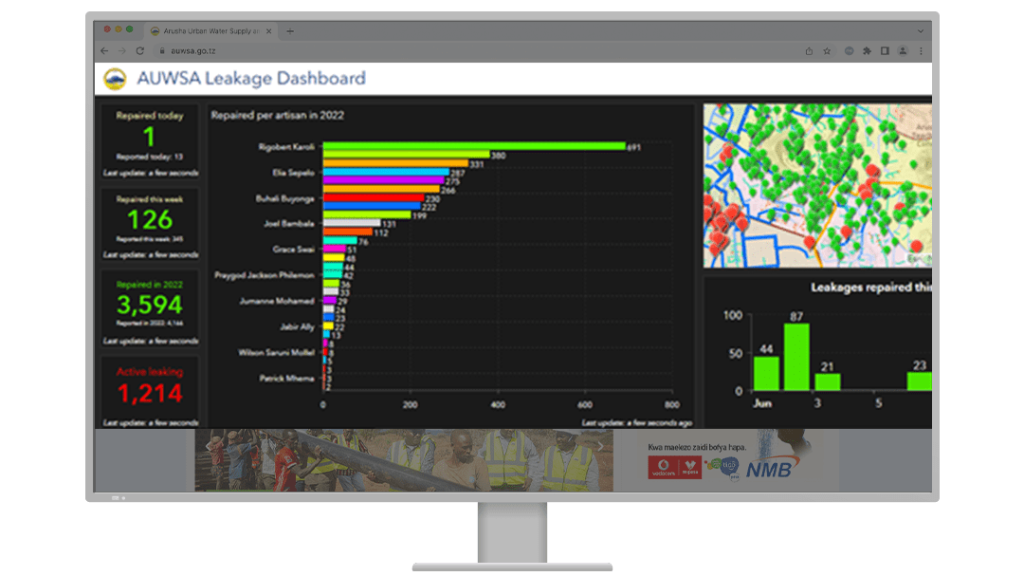
The visualization capabilities of ArcGIS Dashboards were harnessed to gain insights into the number of leaks and their repair progress. Additionally, AUWSA established district metered areas and conducted network isolations to identify problematic pipes. This led to a strategic pipe rehabilitation plan, resulting in an impressive 83 percent reduction in leakage rates and a 6 percent reduction in nonrevenue water.
ArcGIS also played a crucial role in understanding water consumption patterns. It provided analytical tools to identify anomalies, such as meters reporting zero consumption, facilitating prompt issue resolution.
Mitigating unauthorized water connection
To address illegal connections, AUWSA integrated ArcGIS Workforce and Survey123, streamlining the process of surveying and documenting meter statuses. This initiative involved surveying 3,883 houses, uncovering 545 plots with anomalies. Resolving these issues promises to boost revenue in the area significantly.
ArcGIS Dashboards played a key role in tracking project progress and performance measurements for individual workers. This enhanced transparency and improved management of daily operations. Managers could access dashboards on tablets, and large screens displayed data at the main office.
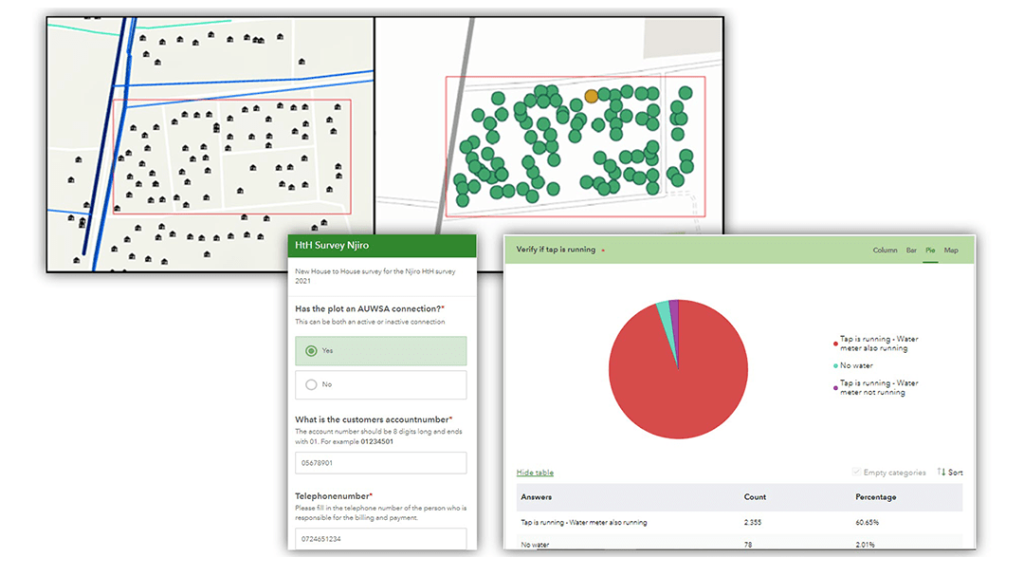
The expansion of water services into remote areas presented another challenge, but ArcGIS assisted in accurately mapping existing infrastructure and managing network expansion. The introduction of handheld Garmin GPS receivers paired with Collector allowed for precise asset location capture.
Key lessons learned include the need for smart devices for field applications, efficient staff training, clear strategy development with management support, and the establishment of a GIS department to serve all organization departments. AUWSA also has plans to use drones for leak identification and inspection of remote areas.
Delivering water and sanitation services
AUWSA’s adoption of ArcGIS has proven to be a transformative step. It has increased data quality, efficiency, and decision-making capabilities, ultimately supporting the utility’s goal of delivering quality water and sanitation services efficiently and effectively. ArcGIS has not only improved daily operations but also set a path for the utility’s future endeavors.
This story was first published by esri.com, view full story here







