Mastering 3D Analysis in ArcGIS: A 2024 Guide for Urban Planners
August 20, 2024 2024-08-20 9:32Mastering 3D Analysis in ArcGIS: A 2024 Guide for Urban Planners
Mastering 3D Analysis in ArcGIS: A 2024 Guide for Urban Planners
Urban planning has always relied on data, maps, and models to design cities that are efficient, sustainable, and livable. With the growing complexity of urban environments and the increasing need for smarter infrastructure, traditional 2D maps are no longer sufficient. This is where 3D analysis – a powerful tool in ArcGIS that allows urban planners to visualize, simulate, and analyze cityscapes in three dimensions comes into play. This 2024 guide explores how urban planners can master 3D analysis in ArcGIS, helping them design better cities and make more informed decisions.
Why 3D Analysis Matters in Urban Planning
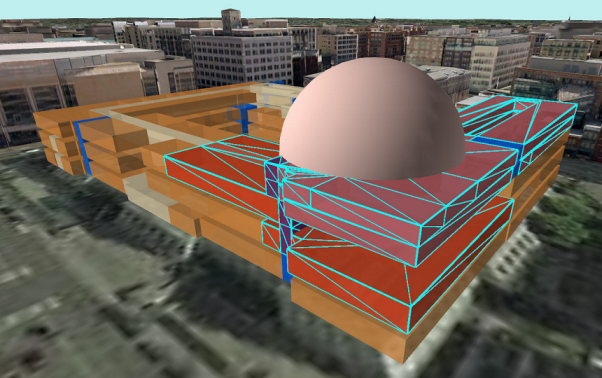
3D analysis in ArcGIS provides urban planners with a more realistic view of urban environments. By incorporating height, depth, and volume into spatial data, planners can better understand how buildings interact with each other, how sunlight affects public spaces, and how infrastructure fits into the broader landscape. In 2024, with advancements in 3D GIS technologies, these capabilities are more accessible and powerful than ever before.
3D analysis is not just about creating visually impressive models; it’s about enhancing the accuracy of urban planning decisions. For example, planners can simulate how a new building will cast shadows at different times of the day, evaluate the visibility of landmarks from various points in the city, and assess the potential impact of new infrastructure on wind patterns or water drainage.
Key Features of ArcGIS for 3D Analysis
ArcGIS offers a suite of tools and features designed specifically for 3D analysis. Understanding these tools is crucial for urban planners looking to fully leverage the power of 3D GIS in their projects.
1. ArcGIS Pro
ArcGIS Pro is the flagship desktop application for working with 3D GIS. It supports the creation and analysis of 3D data, offering a range of tools for urban planning, including:
- Scene Layers: Manage and visualize large volumes of 3D data, such as buildings, trees, and other city features, within a 3D environment.
- 3D Editing: Edit features directly in 3D, allowing for the precise placement and adjustment of buildings, roads, and other infrastructure.
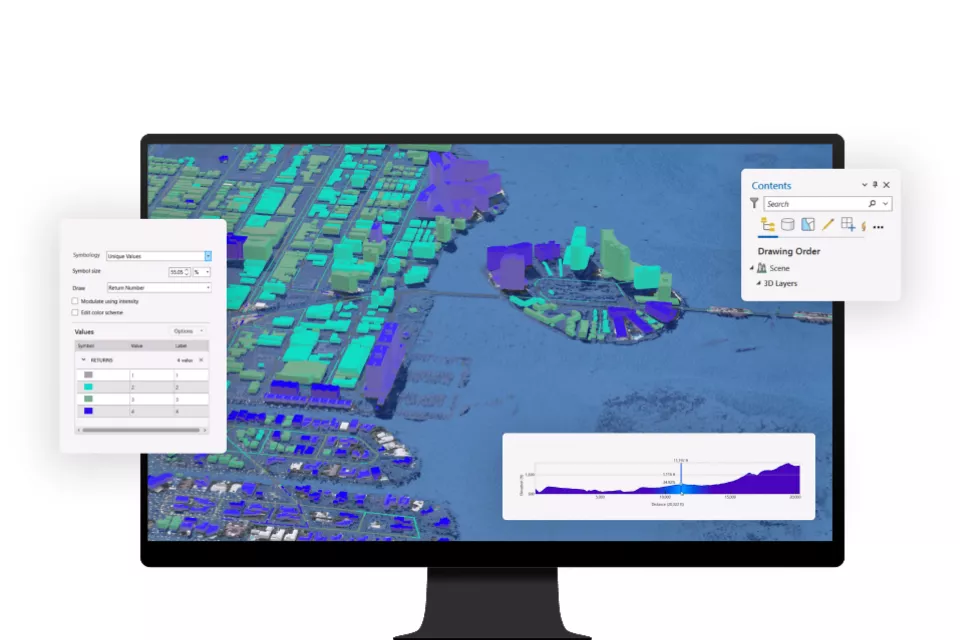
- Terrain Analysis: Analyze elevation data to understand how terrain impacts urban development, infrastructure placement, and flood risk.
2. ArcGIS CityEngine
ArcGIS CityEngine is a specialized tool for 3D urban design. It allows urban planners to create detailed, large-scale 3D city models quickly. With procedural modeling, planners can generate entire city blocks, apply architectural styles, and explore different design scenarios.
CityEngine’s ability to integrate with ArcGIS Online means that 3D models can be shared and collaborated on easily, making it an invaluable tool for large planning teams or public consultations.
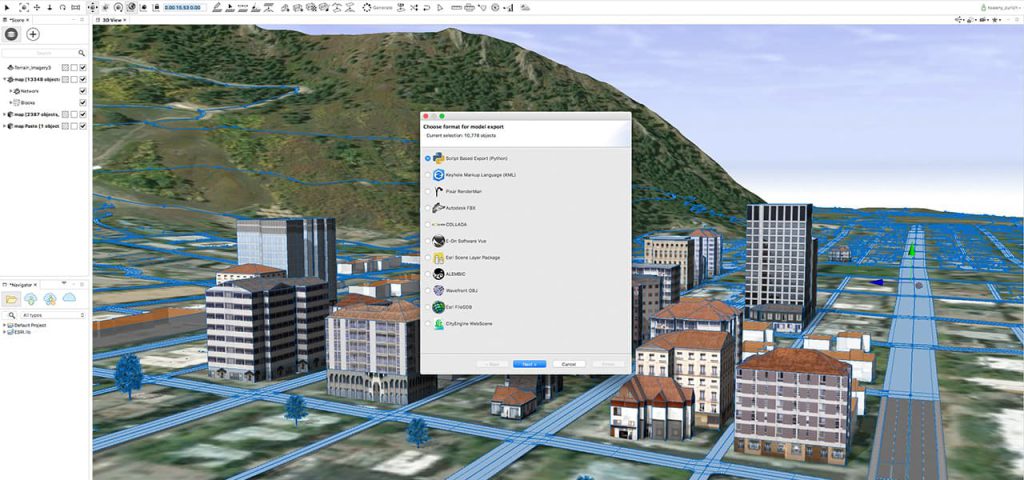
3. ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Urban
ArcGIS Online extends 3D analysis capabilities to the web, allowing for the sharing and visualization of 3D models in a cloud-based environment. This is particularly useful for engaging stakeholders and the public in urban planning projects.
ArcGIS Urban, a web-based application built on ArcGIS Online, is specifically designed for urban planning and includes tools for zoning, land-use planning, and scenario-based design. It allows planners to create and evaluate different development scenarios in a 3D context, facilitating more informed decision-making.
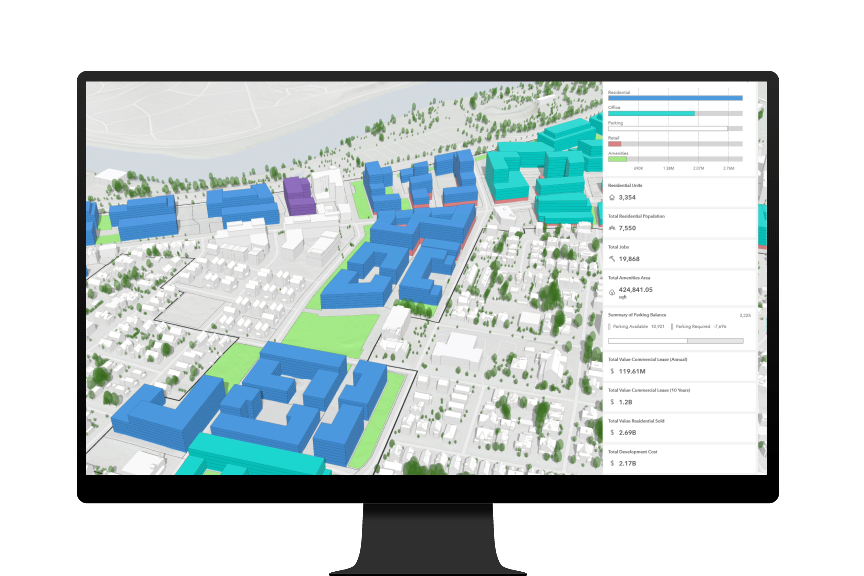
Practical Applications of 3D Analysis in Urban Planning
3D analysis in ArcGIS is not just theoretical; it has practical applications that can significantly impact urban planning outcomes. Here are some of the most important ways that urban planners can use 3D analysis in 2024:
1. Shadow and Solar Analysis
As cities become denser, the impact of shadows on public spaces and buildings is a growing concern. ArcGIS Pro enables planners to perform detailed shadow analysis, determining how new buildings will affect sunlight exposure throughout the day and year. This is crucial for designing livable cities where public spaces receive adequate sunlight and where building design maximizes natural light.
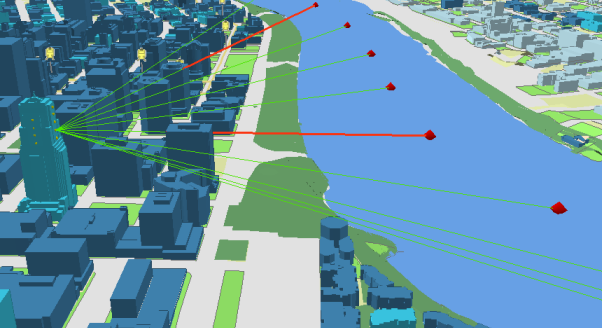
2. Visibility and Line of Sight Analysis
In urban design, understanding visibility is essential for everything from advertising to ensuring public safety. With 3D analysis in ArcGIS, planners can assess the visibility of landmarks, important infrastructure, or signage from different locations and viewpoints. This analysis helps in planning the placement of buildings, roads, and public spaces to enhance visibility and accessibility.
3. Infrastructure Planning and Simulation
Urban infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and utilities, often needs to be analyzed in three dimensions to understand its impact fully. ArcGIS allows planners to simulate how new infrastructure will interact with the existing environment, including the terrain and surrounding buildings. This can prevent costly mistakes and ensure that infrastructure projects are well-integrated into the city fabric.
4. Flood Risk and Water Management
Flooding is a significant concern in many cities, and 3D analysis provides a way to model and predict flood risks more accurately. By analyzing terrain, water flow, and drainage systems in three dimensions, planners can design better flood prevention measures and plan infrastructure to minimize flood risk.
5. Transportation and Mobility Planning
3D analysis in ArcGIS also supports transportation planning by enabling planners to visualize and assess the impact of new roads, transit lines, and other transportation infrastructure. This includes analyzing how these elements interact with the city’s topography and existing urban layout, as well as their impact on traffic flow and accessibility.
Tips for Mastering 3D Analysis in ArcGIS
To truly master 3D analysis in ArcGIS, urban planners should focus on continuous learning and practical application. Here are some tips to help you get started:
- Start with the Basics: If you’re new to 3D GIS, begin by exploring the 3D capabilities in ArcGIS Pro. Familiarize yourself with the basic tools, such as 3D editing, scene layers, and terrain analysis.
- Use Real-World Data: Practice your skills using real-world data from your city or region. This will give you a better understanding of how 3D analysis can be applied to actual urban planning challenges.
- Experiment with CityEngine: ArcGIS CityEngine is a powerful tool for creating detailed urban models. Take the time to learn procedural modeling techniques to rapidly generate and modify large-scale cityscapes.
- Engage with the Community: Join online forums, attend webinars, and participate in ArcGIS user groups. Learning from other professionals’ experiences can provide valuable insights and tips.
- Stay Updated: The world of GIS is constantly evolving. Keep up with the latest updates and features in ArcGIS by following Esri’s blog, attending conferences, and taking advantage of online training resources.
3D analysis in ArcGIS is transforming urban planning, making it possible to design more efficient, sustainable, and visually appealing cities. As we move further into 2024, the capabilities of ArcGIS for 3D analysis will continue to grow, providing urban planners with even more tools to tackle the challenges of modern urbanization. By mastering these tools, planners can create cities that are not only functional but also vibrant and resilient for generations to come.