The Importance of Data Accuracy and Validation in GIS Projects
June 18, 2024 2024-06-18 13:58The Importance of Data Accuracy and Validation in GIS Projects
The Importance of Data Accuracy and Validation in GIS Projects
In the realm of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), data is the backbone that supports all analyses, visualizations, and decision-making processes. Ensuring data accuracy and validation is critical for the success and reliability of any GIS project. Inaccurate or unvalidated data can lead to flawed analyses, misinformed decisions, and costly errors. This blog post delves into the significance of data accuracy and validation in GIS projects, the challenges faced, and best practices to ensure high-quality geospatial data.
Read more: Tips & Tricks: Field Data Collection Best Practices
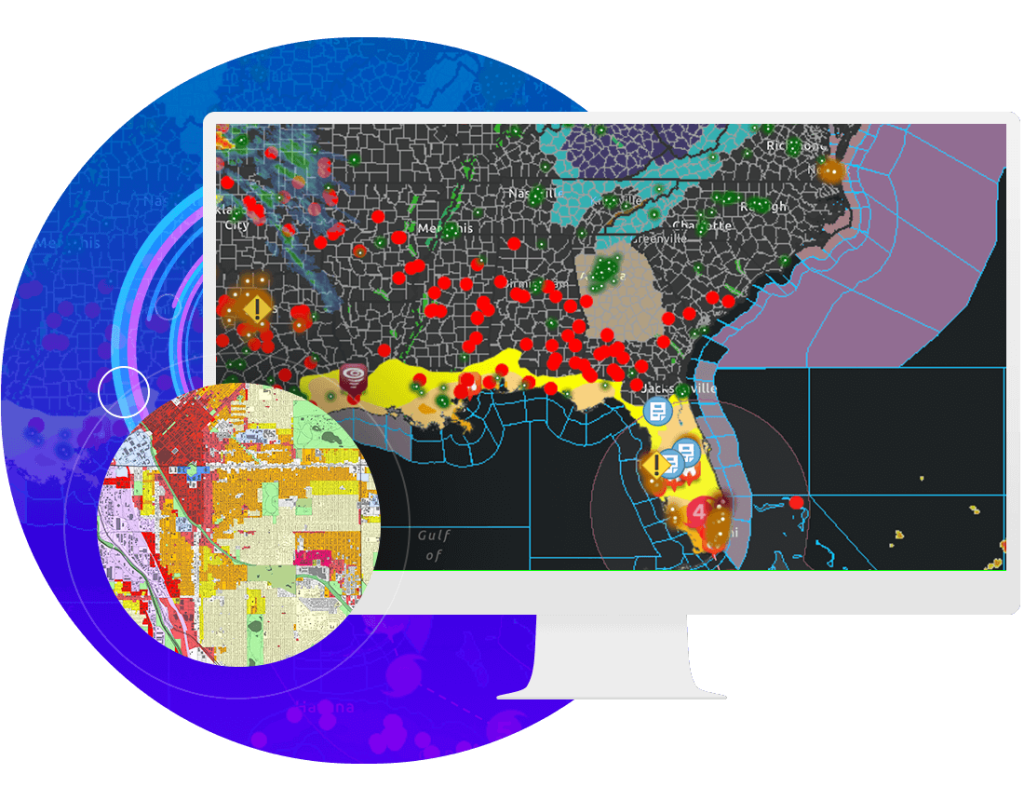
Understanding data accuracy in GIS
Data accuracy in GIS refers to how closely the data represents the real-world conditions it aims to depict. It encompasses several dimensions:
- Positional accuracy: This measures how accurately the locations of geographic features on the map match their true positions on the ground. High positional accuracy is essential for applications such as urban planning, navigation, and environmental monitoring.
- Attribute accuracy: This pertains to the correctness of the descriptive information associated with geographic features. For example, in a land-use map, the attribute data must accurately reflect the actual land uses.
- Temporal accuracy: This involves the correctness of data regarding the time period it represents. Temporal accuracy is crucial for time-sensitive analyses, such as tracking environmental changes or monitoring urban growth.
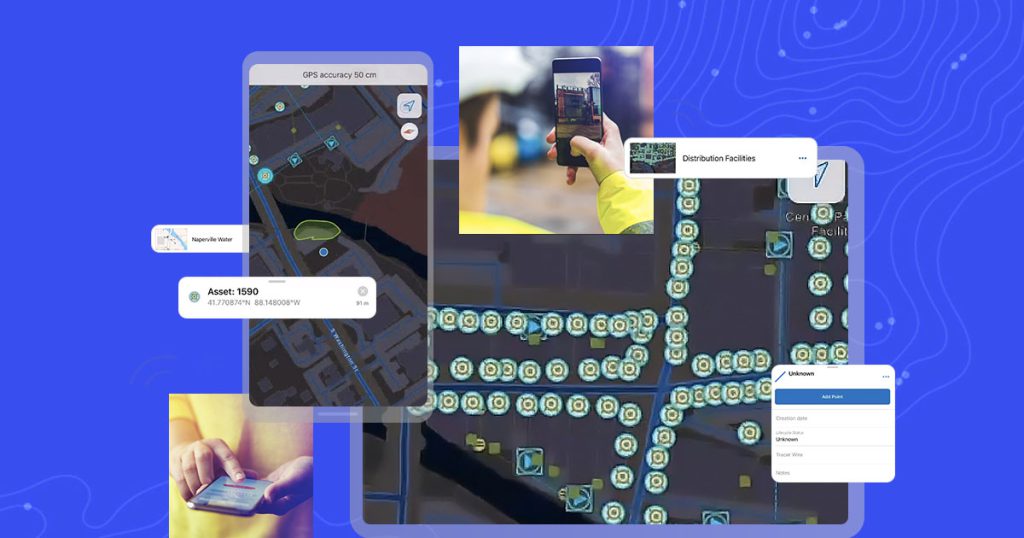
The role of data validation
Data validation is the process of ensuring that the data collected meets the required quality standards and is suitable for its intended use. It involves checking for errors, inconsistencies, and gaps in the data. Validation helps to identify and rectify issues that could compromise the integrity of GIS analyses and outputs.
Why data accuracy and validation matter
- Informed decision-making: Accurate and validated data provides a reliable foundation for decision-making. In sectors such as public health, disaster management, and infrastructure development, decisions based on precise data can significantly impact outcomes and lives.
- Cost efficiency: Investing in data accuracy and validation can prevent costly mistakes. Errors in geospatial data can lead to incorrect analyses, which might result in financial losses, project delays, or the need for costly rework.
- Credibility and trust: High-quality data enhances the credibility of GIS projects and the trust stakeholders place in them. Reliable data ensures that stakeholders, including government agencies, businesses, and the public, can confidently rely on the findings and recommendations derived from GIS analyses.
- Regulatory compliance: Many industries are subject to regulations that mandate specific standards for data accuracy and quality. Ensuring data accuracy and validation helps organizations comply with these regulations and avoid potential legal and financial repercussions.
Read more: From the Field to Map: Collecting and Analyzing Data With ArcGIS
Challenges in ensuring data accuracy and validation
- Data collection methods: Variability in data collection methods can lead to inconsistencies and errors. Standardizing data collection procedures is essential to maintain accuracy.
- Data integration: Integrating data from multiple sources can introduce errors if the data sets are incompatible or if there are discrepancies in data formats and scales.
- Human error: Manual data entry and processing are prone to human errors. Automated data validation tools and processes can help minimize these errors.
- Dynamic nature of data: Geospatial data is often dynamic, with features and attributes changing over time. Regular updates and validation are necessary to keep the data current and accurate.

Best practices for ensuring data accuracy and validation
- Standardize data collection procedures: Establishing standardized procedures for data collection ensures consistency and accuracy. Training data collectors and using reliable equipment are critical components of this process.
- Implement automated validation tools: Leveraging automated tools for data validation can help identify and correct errors more efficiently than manual methods.
- Regularly update and review data: Geospatial data should be regularly updated and reviewed to maintain its accuracy and relevance. Implementing a schedule for periodic data audits can help in this regard.
- Use high-quality data sources: Whenever possible, use data from reputable and high-quality sources. Ensuring that the data providers have robust accuracy and validation protocols in place can save time and resources.
- Document data processes: Maintaining comprehensive documentation of data collection, processing, and validation procedures helps ensure transparency and consistency. This documentation is also invaluable for troubleshooting and improving data quality over time.
The importance of data accuracy and validation in GIS projects cannot be overstated. High-quality geospatial data is the cornerstone of effective analysis, reliable decision-making, and successful project outcomes. By prioritizing data accuracy and implementing robust validation processes, GIS professionals can enhance the integrity and impact of their work, ultimately contributing to more informed and effective solutions to real-world challenges.






Comment (1)
Puteh Fatimah Muniram
Good