Unlocking Spatial Analysis: Top Tools in ArcGIS for Data-Driven Decisions
November 5, 2024 2024-11-05 9:01Unlocking Spatial Analysis: Top Tools in ArcGIS for Data-Driven Decisions
Unlocking Spatial Analysis: Top Tools in ArcGIS for Data-Driven Decisions
In the world of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), ArcGIS stands as one of the most powerful platforms for conducting spatial analysis. With tools that enable in-depth spatial insights, ArcGIS supports data-driven decisions across various fields, including urban planning, environmental management, transportation, and public health. Let’s dive into some of the top spatial analysis tools in ArcGIS that can help you make informed decisions based on location-based insights.
Related: Three Things ArcGIS Spatial Analyst Can Do for You
1. Proximity Analysis
Proximity analysis is essential in scenarios where distance plays a key role, such as determining access to services, assessing disaster risk areas, or identifying underserved regions. ArcGIS’s Buffer tool allows users to create buffer zones around points, lines, or polygons to analyze areas within a specific distance. For instance, a healthcare planner can use proximity analysis to identify neighborhoods with inadequate access to medical facilities, enabling targeted intervention.
2. Overlay Analysis
Overlay analysis is the process of combining multiple layers to understand the relationship between different variables within the same geographic area. Tools like Intersect, Union, and Erase allow GIS professionals to combine datasets and draw meaningful insights from overlapping layers. For example, in urban planning, overlaying zoning data with environmental risk maps helps planners identify areas where development is limited or needs special attention, such as flood-prone zones.
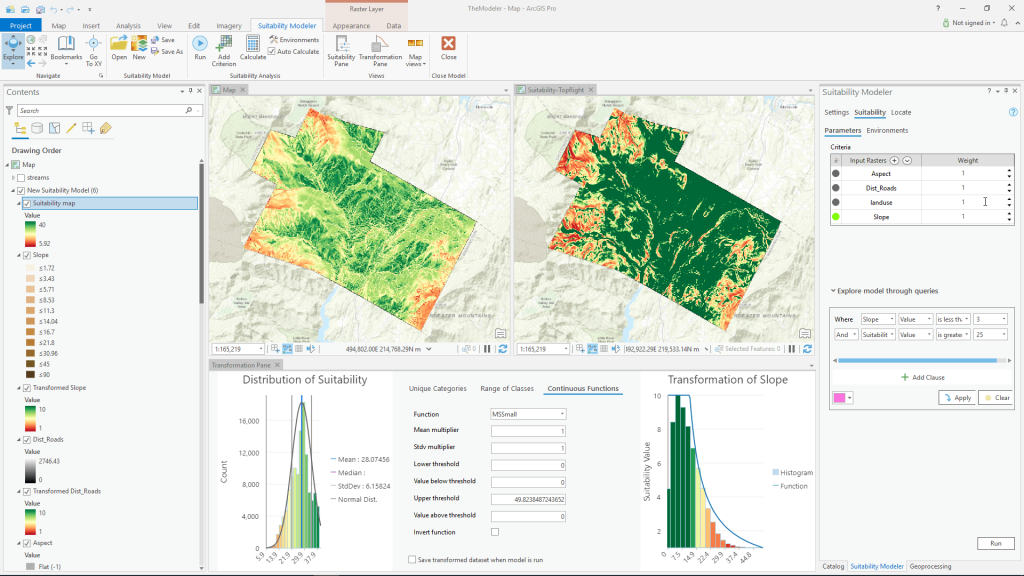
3. Suitability Modeling
Suitability modeling is used to identify optimal locations based on certain criteria. The Weighted Overlay tool in ArcGIS allows users to assign weights to multiple layers—like slope, soil quality, or land cover—to identify the best areas for specific projects, such as building sites or conservation areas. Suitability modeling is critical for sectors like agriculture and conservation, where factors like soil type, climate, and terrain are crucial.
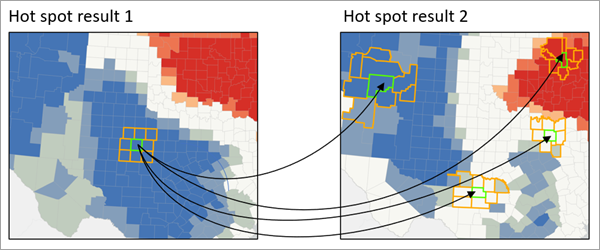
4. Hot Spot Analysis
Hot Spot Analysis is essential for identifying statistically significant clusters of high or low values within a dataset. The Getis-Ord Gi (Hot Spot) tool* in ArcGIS helps pinpoint areas of significant activity or trends, such as crime hotspots in urban areas or disease outbreaks in public health. By identifying these clusters, organizations can allocate resources effectively and address issues proactively.
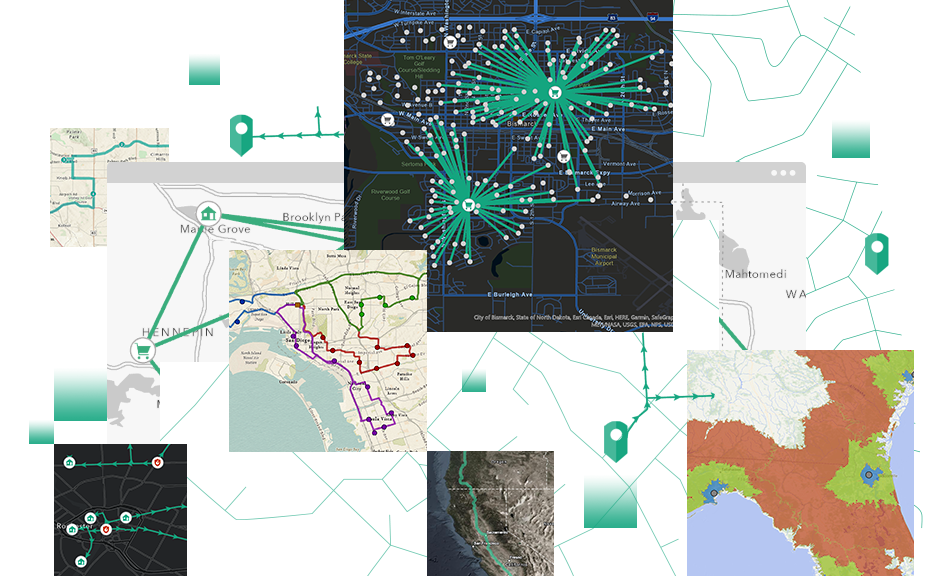
5. Network Analysis
Network analysis tools allow users to analyze routes, accessibility, and service areas within a transportation network. With tools like Closest Facility, Service Area, and Route, ArcGIS enables the calculation of optimal paths, helping businesses and municipalities improve logistics and emergency response planning. For instance, logistics companies can use network analysis to optimize delivery routes, reducing time and costs.
Related: 3 Things ArcGIS Network Analyst Can Do for You
ArcGIS’s spatial analysis tools provide powerful insights into geographic data, allowing professionals to make data-driven decisions based on location-based patterns and relationships. By harnessing tools like proximity analysis, overlay analysis, suitability modeling, hot spot analysis, and network analysis, GIS professionals can unlock the full potential of spatial analysis to enhance decision-making, drive efficiency, and tackle complex spatial challenges.
Learn more here: https://ea-store.esri.com/en-ke/store/overview